Hydraulic Fracturing Biocides
Biocides for Hydraulic Fracturing Fluid Applications
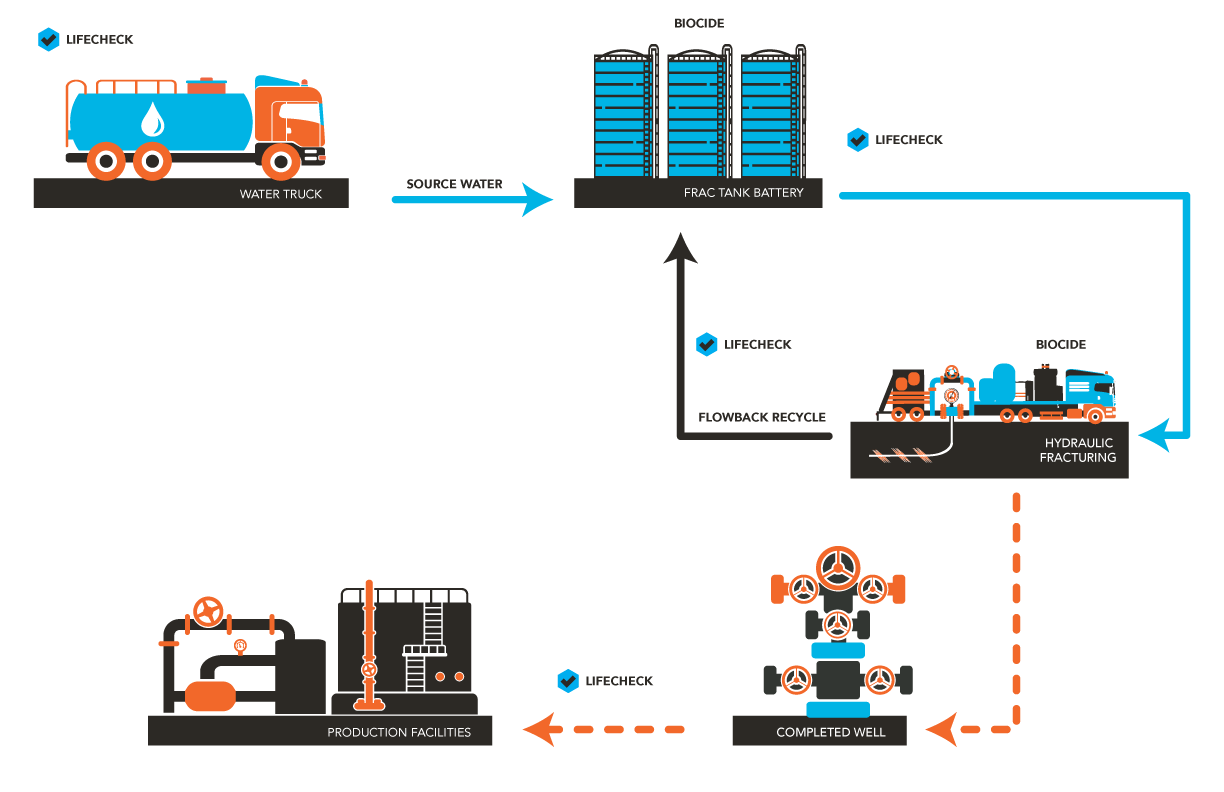
Hydraulic fracturing utilizes large volumes of water to achieve improved hydrocarbon recovery. These fluid and proppant systems may vary in formula, but the carrier waters used will inevitably contain varying levels of microbes that have the potential to cause long term issues downhole. Many reservoirs provide conditions optimal for microbial growth, and upon introduction by fracturing operations, can contaminate the reservoir by establishing communities in the fracture networks.
The primary issues caused by a microbiologically contaminated reservoir are souring (H2S production by sulfide producing microbes) and microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC). MIC may occur within the wellbore, or the microbes may be carried throughout an entire gathering system and into processing facilities potentially increasing corrosion risk of many assets.
In order to prevent microbial related issues, registered biocides can be applied at appropriate places in the hydraulic fracturing process to maintain microbial control. This ensures the health of the well not only during initial recovery but for the remaining production life.
Application
An effective biocide program for hydraulic fracturing considers microbial growth conditions at surface to ensure fluid system stability, as well as downhole conditions for reservoir protection. The application of a biocide in completion activities requires attention to:
- source water chemistry
- contamination points on site
- compatibility with frac chemicals used
- downhole environment
- storage conditions (asset layup)
- water re-use initiatives
- post frac shut in times
Execution of a biocide program may include a biocide selection study during completion design to choose a compatible chemistry and optimized dosage rate. Our LifeCheck Assess method employs a full process review of the completion design and an appropriate chemistry study with raw source waters. This study will set a baseline program that can be adjusted on site with application recommendations for the most effective and logistically appropriate place within the operation.
Biocide choices are made not only on kill efficacy, but also on the compatibility with every area and environment in the completion process, up to and including the length of time hydraulic fracturing waters will be contacting the reservoir. OSP maintains a suite of registered biocides backed by expertise and experience in applications across North America.
Microbial Testing
Testing microbial levels and ensuring control limits are being maintained is an important part of any biocide application. LifeCheck ATP testing technology generates total active microbial readings on site within minutes. This allows for evaluation of real time water management on site. Immediate microbial readings can identify problem areas contributing to contamination, ensure rapid kill efforts are working at surface, and ensure dosages can be adjusted effectively during operational down time, or when changes must be made on the fly.
Looking for a metered application?
2K7 Solution
Effective in high volume applications where liquid handling equipment allows for plug and play
- Pre Treat Tanks
- Post Oxidizer Treatment
- On the Fly at Blender or Chem Add
- Topping up Buffer/Working Tanks
- Fluid Transfer Control (Trucking, Pipeline, Lay Flat Hosing)
- Fluid Staging – Tanks or Pits (Long Term Control)
- Asset Layup or Cleaning
DB7 Solution
Effective in high volume applications where liquid handling equipment allows for plug and play
- Pre Treat Tanks
- On the Fly at Blender or Chem Add
- Topping up Buffer/Working Tanks
- Fluid Transfer Control (Trucking, Pipeline, Lay Flat Hosing)
- Asset Layup or Cleaning
GQ123
Effective in high volume applications where liquid handling equipment allows for plug and play
- Pre Treat Tanks
- Post Oxidizer Treatment
- On the Fly at Blender or Chem Add
- Topping up Buffer/Working Tanks
- Fluid Transfer Control (Trucking, Pipeline, Lay Flat Hosing)
- Fluid Staging – Tanks or Pits (Long Term Control)
- Asset Layup or Cleaning
GQ 2510
Effective in high volume applications where liquid handling equipment allows for plug and play
- Pre Treat Tanks
- Post Oxidizer Treatment
- On the Fly at Blender or Chem Add
- Topping up Buffer/Working Tanks
- Fluid Transfer Control (Trucking, Pipeline, Lay Flat Hosing)
- Fluid Staging – Tanks or Pits (Long Term Control)
- Asset Layup or Cleaning
Looking to prevent water hauling?
2K7 Bugsticks
Use in low water volume and limited (restricted) access applications
- Pre Treat Tanks
- Fluid Transfer Control (Trucking, Pipeline, Lay Flat Hosing)
- Asset Layup or Cleaning
2K7 Water Soluble Paks
Avoids chemical contact
- Pre Treat Tanks
- Topping up Buffer/Working Tanks
- Fluid Transfer Control (Trucking, Pipeline, Lay Flat Hosing)
- Fluid Staging – Tanks and Pits (Long Term Control)
- Asset Layup or Cleaning
Are you evaluating options?
Talk to our Experts
Wherever there is water there are microbes. Depending on the application, microbial contamination can lead to serious issues such as fouling, souring and corrosion. Contact our team of experts to learn more about biocides for hydraulic fracturing fluid applications. We are here to help you avoid downtime, safety issues and equipment failure.
Killing it in Completions
When asked about frac kill studies, Virginia Wornstaff, CTO, responded with some words of wisdom from her extensive experience. During frac operations, frac studies are often run for the duration – often a 48 hour test. Regularly, the waters are in the reservoir for a lot longer when taking into consideration the time before load waters are fully recovered. Also, the time between frac and production facility tie in can take weeks or even months. Based on this, the selected biocide will be challenged to maintain control for this extension in time. When working with clients who get random well souring in fields with consistent frac programs and treatments, we often see the difference is in the time between frac and production activities. This extension of time creates a little incubator full of warm, stagnant, nutrient-rich conditions. Now in charge of disrupting this reservoir Petri dish, the treatment program should be adjusted to compensate for the new performance demand. Completing a three-week study or a re-inoculation procedure allows for measurement of residual biocide effects after extended periods of time. With a goal of preventing long-term contamination of the reservoir, wellhead testing 30 days after your well comes on production is going to give you the best indication of success.